Mission of Japan Standard Time Group
Comparison of JST
- Comparison with International Time
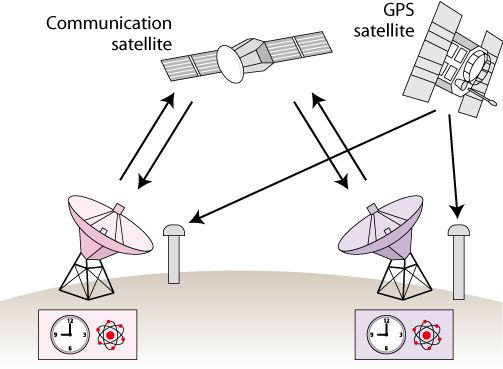
There are two methods to compare International Time: One is performed by
GPS satellites constructed in the U.S.A. Another is by communication Satellites.
GPS satellites mount highly accurate atomic clocks and are used all over
the world. Car navigation systems are typical and popular for the general
user. The radio waves transmitted from GPS satellites contain time information,
and this is the GPS time. By receiving this GPS time and comparing it with
the clocks settled in each station, the time difference between the GPS
time and the local station time can be measured.
Standard organizations in the world perform these GPS
time comparison by common-view method.
Calculating the data obtained by each standard station makes it possible
to measure the time difference between GPS time and each standard clock.
With the use of simultaneously observed data, time
comparison between two standard stations is made with a precision of one hundred-millionths
or even billionths of a second.
Another time comparison is done by the communication satellite. Our Group
collaborates with other standard organizations, National Institute of Advanced
Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), Germany, Australia, U.S.A, China,
Taiwan, Korea, and Singapore, in continuous experiments on regular Two-Way
Satellite Time and Frequency Transfer (TWSTFT) using commercial communication
satellites. Each station sends time
information respectively through communication satellite and uses it to
calculate time difference between stations.
With the above method, time
comparison is made with a precision of one billionth to ten-billionths of a
second.


left : Two-way satellite time and frequency transfer method
right : GPS common view method
- International Comparison of UTC
The both data of the time comparison between GPS time and UTC (NICT) obtained
regularly, and that of TWSTFT are sent to the International Organization
of Weights and Measures (BIPM) in France.
At the BIPM, International Atomic Time (TAI) and Coordinated Universal
Time (UTC) are determined based on the time comparison data obtained, with
the same method, by the organizations all over the world.
The UTC (NICT) is generated and maintained in order to keep the difference
between the UTC and the UTC (NICT) below ± 10 nanoseconds (1 nanosecond = 1/1,000,000,000 second).

(Click the picture above to see larger picture)
