Mission of Japan Standard Time Group
New Initiatives for an IT Society
- Electronic Time Authentication
Dramatic progress in electronic commerce and electronic fund transfers, in addition to the launch of the electronic government project beginning in FY 2003, has led to a demand for a precise, publicly authorized time standard for electronic procedures.
The concept of incorporating precise time into advanced information society is eferred to as new words “time business,” which mainly consists of “time dissemination” and “time authentication” business. The IT community has been encouraged to adopt precise time; e.g., as a
timestamp. A Japanese law concerning reliability of electronic documents (commonly called "e-documents law") which came into effect in April 2005, requires time stamps to be put on electronic documents to certify that they have not been altered, and it is inevitable for precise time information to be used for the time stamps.
In response to the needs of society, the JSTG began disseminating Japan Standard Time, which is internationally traceable and widely available in the general public, in an easy-to-use format for issuing time stamps in February 2005. This has made it possible to use precisely and socially authorized electronic time information.
At the beginning of this service, time stamps were issued only through a certification system by a voluntary organization. However, in line with trends in other countries, a national certification system was launched in July 2021.
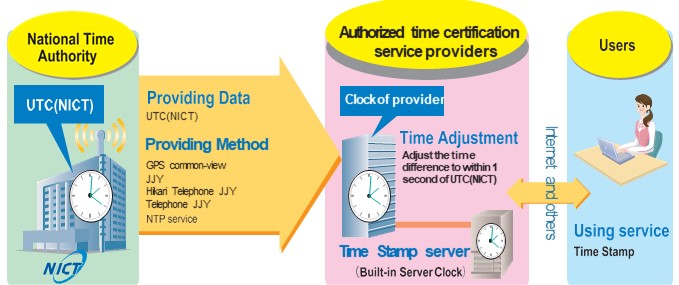
As shown in the figure below, National Institute of Information and Communications Technology, as a National Time Authority (NTA), disseminates Japan Standard Time (UTC(NICT)) to the authorized time certification service providers. The authorized providers maintain their timescale so that the difference between their own clocks and Japan Standard Time is within one second. As a result, a system has been built in which time traceable to Japan Standard Time is disseminated (timestamps are provided) to users. For the dissemination of Japan Standard Time, the Hikari Telephone JJY and NTP provided by the JSTG are used.
And the JSTG has promoted the use of traceability chains of UTC (NICT) to the authorized provider and the structure of the time dissemination and the audit carried out by the authorized provider. Technical requirements for the authorized provider have been established in Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS X 5094) and also established in ISO/IEC 18014-4 by the International Organization for Standardization.
(Click the picture above to see larger picture)